The weight difference of steel and nanocomposite rebar (GFRP)
The reason for the importance of The weight difference of steel and nanocomposite rebar is that the most obvious feature of nano products is maintaining or increasing the quality and efficiency of that product in much less weight and volume.
Introduction
Reinforcement bars, commonly known as rebar, are crucial components in construction, providing tensile strength to concrete structures. Traditionally, steel rebar has been the go-to material for this purpose. However, advancements in material science have led to the development of nanocomposite rebar, which offers several advantages, including weight reduction. This article explores the weight differences between steel and nanocomposite rebar, their implications for construction, and the benefits of using lighter materials.
What is a Steel Rebar?
A steel rebar is a steel bar or mesh of steel wires used as a tension device in reinforced concrete and masonry structures. It is designed to expand and contract with concrete, providing the necessary tensile strength to withstand various loads. Steel rebar is known for its durability, strength, and resistance to corrosion when properly treated.
Weight of Steel Rebar
The weight of steel rebar varies depending on its diameter and length. The standard weight of steel rebar is approximately 0.668 pounds per foot for a #3 bar (3/8 inch diameter) and can go up to 2.668 pounds per foot for a #11 bar (1-3/8 inch diameter). This weight can significantly impact the overall weight of a concrete structure, especially in large-scale projects.
What is Nanocomposite Rebar?
Nanocomposite rebar is a newer innovation in the construction industry, made from a combination of polymers and nanomaterials. This type of rebar is designed to provide similar or superior strength to traditional steel rebar while being significantly lighter. The incorporation of nanomaterials enhances the mechanical properties of the polymer matrix, resulting in a product that is both strong and lightweight.
Weight of Nanocomposite Rebar
Nanocomposite rebar typically weighs much less than its steel counterpart. For instance, a nanocomposite rebar of similar dimensions to a #3 steel rebar may weigh only about 0.3 pounds per foot, while a #11 nanocomposite rebar might weigh around 1.0 pounds per foot. This substantial weight reduction can lead to significant savings in transportation and handling costs during construction.
The weight difference of steel and nanocomposite rebar
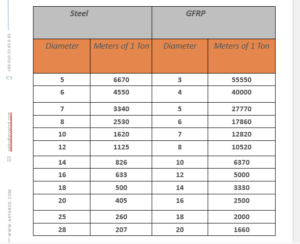
When comparing the weights of steel rebar and nanocomposite rebar, the differences are striking. Here’s a quick comparison based on standard sizes:
As illustrated in the table, nanocomposite rebar can weigh up to 55% less than steel rebar, depending on the size. This weight difference can have significant implications for construction projects.
Implications of Weight Differences
1. Transportation and Handling
The lighter weight of nanocomposite rebar translates to lower transportation costs. Construction companies can transport more material in a single load, reducing the number of trips required. Additionally, the ease of handling lighter materials can lead to faster installation times on-site, improving overall project efficiency.
2. Structural Design Flexibility
With the reduced weight of nanocomposite rebar, engineers have more flexibility in their structural designs. Lighter materials can allow for the construction of taller buildings or longer spans without the need for additional support. This flexibility can lead to innovative architectural designs that were previously impractical with traditional steel rebar.
3. Reduced Foundation Requirements
The overall weight reduction in structures using nanocomposite rebar can lead to less stress on foundations. This means that foundations can be designed smaller and lighter, resulting in further material savings and reduced construction costs.
4. Environmental Impact
Using lighter materials like nanocomposite rebar can also have positive environmental implications. Reduced transportation needs lead to lower fuel consumption and emissions. Additionally, the potential for using less concrete in foundations and structures can further decrease the carbon footprint of construction projects.



